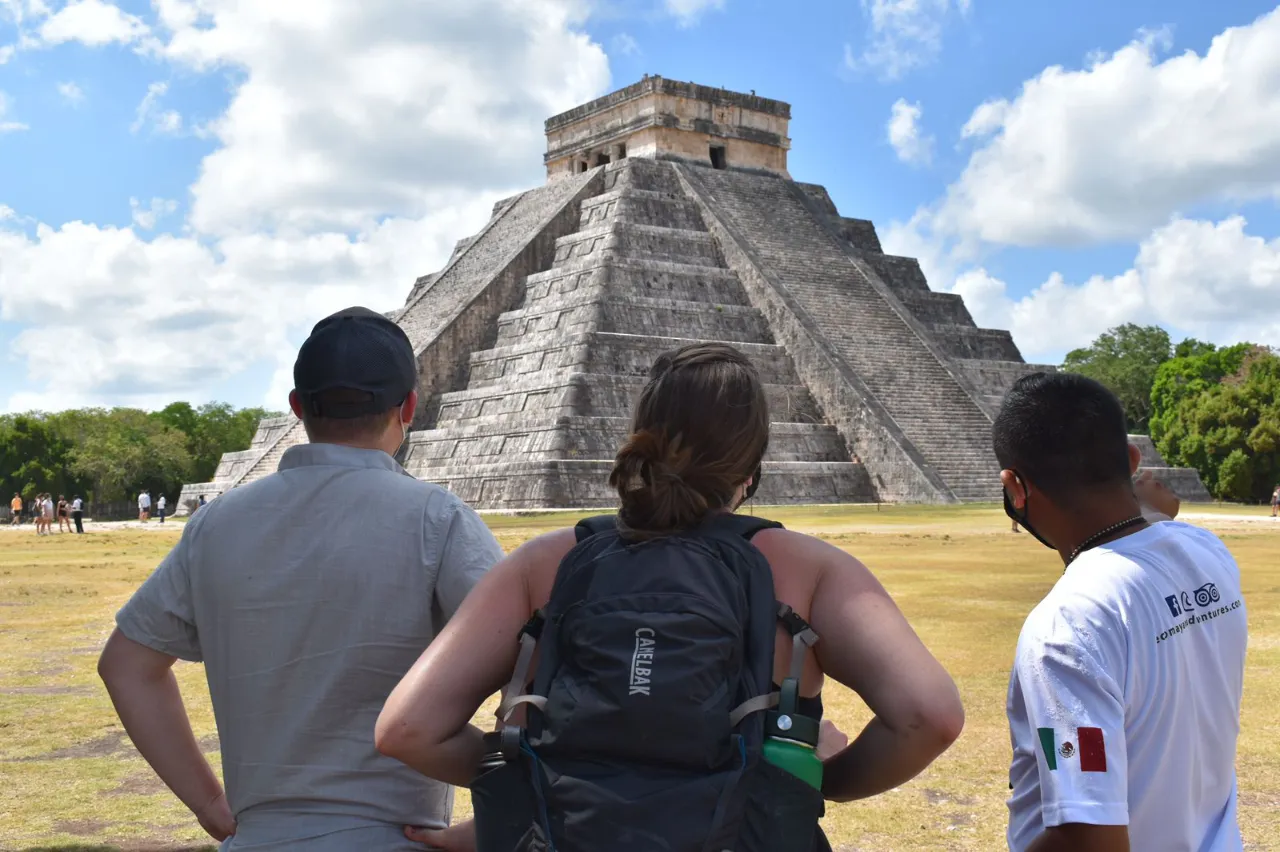
Yucatán Chichén Itzá is a renowned archaeological site that showcases the grandeur of the ancient Maya civilization. Its rich history and stunning architecture make it one of Mexico’s most significant cultural treasures. This article explores its historical significance, architectural marvels, and the challenges it faces today. A comparison with nearby Mayan ruins, such as Ek Balam, Uxmal, and Tulum, will also be included to provide insights for travelers interested in this fascinating region.

 The warrior imagery depicted throughout the temple hints at the militaristic values upheld by the society at the time. The intricate reliefs serve as both decorative elements and historical records of the region’s conquests and battles. The alignment of the Temple of the Warriors with celestial bodies further emphasizes its importance in religious and ceremonial practices.
The warrior imagery depicted throughout the temple hints at the militaristic values upheld by the society at the time. The intricate reliefs serve as both decorative elements and historical records of the region’s conquests and battles. The alignment of the Temple of the Warriors with celestial bodies further emphasizes its importance in religious and ceremonial practices.
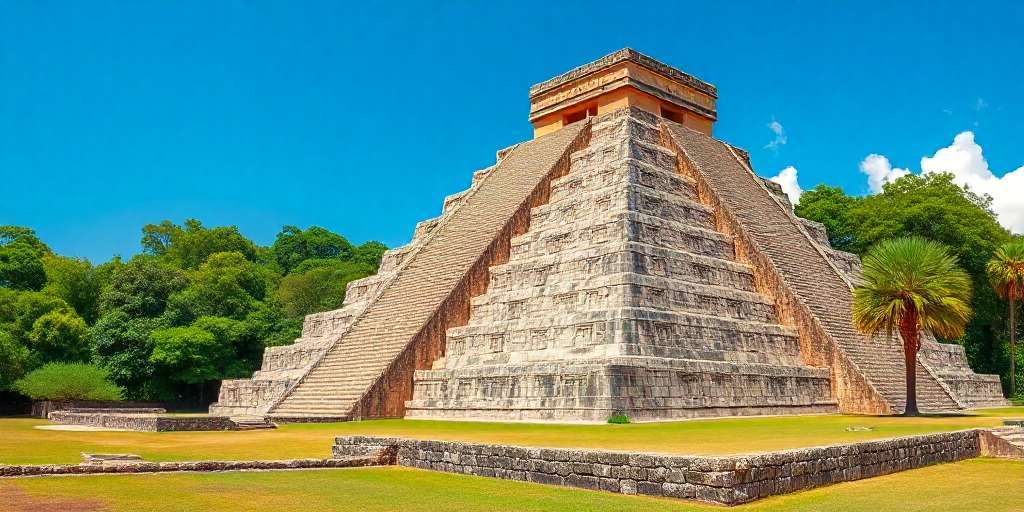


The Historical Significance of Yucatán Chichén Itzá
Chichén Itzá holds immense historical importance within the context of Maya civilization and cultural evolution. It reflects the remarkable achievements and complexities of the societies that inhabited this region.Overview of Chichén Itzá’s Origins
The origins of Chichén Itzá date back to the early centuries of the first millennium. Settlements began to form around natural resources, particularly water sources like cenotes. This strategic location allowed the city to thrive, making it an essential center for trade and religious activities. Initially, the city emerged during the Classic period, reflecting typical Maya architectural styles and serving as a hub for various cultural and economic exchanges. Its name, meaning “at the mouth of the well of the Itzá,” signifies its connection to both the physical landscape and the people who inhabited it.The Classic Period and Its Influence
Chichén Itzá reached its zenith during the Classic Period, particularly between 600 and 1200 AD. This era saw the city flourish in terms of influence, trade, and population growth. The architectural innovations of this time, characterized by elaborate temples and ceremonial platforms, showcased advancements in engineering and artistry. During this period, Chichén Itzá became a melting pot, absorbing diverse influences from neighboring civilizations. This cosmopolitan nature contributed significantly to its development, resulting in the fusion of cultural elements and the evolution of artistic expression within the city.The Role of the Maya and Toltec Civilizations
The Maya civilization was intrinsic to the development of Chichén Itzá, establishing it as a political and religious center. The city became a focal point for various Mayan city-states, facilitating a rich tapestry of cultural interactions.- The arrival of the Toltecs in the 10th century marked a significant turning point. Borrowing elements from Toltec culture, Chichén Itzá integrated new architectural styles and religious practices.
- Notable figures from this era, such as Ce Acatl Topiltzin Quetzalcoatl, greatly influenced the region’s power dynamics, promoting a unique blend of Maya and Toltec ideologies.
Architectural Marvels of Chichén Itzá
The architectural wonders of Chichén Itzá reflect the ingenuity and artistic accomplishments of the Maya civilization. Each structure serves as a testament to their advanced understanding of engineering, astronomy, and cultural symbolism. The following sections explore some of the most iconic structures within this remarkable site.The Temple of Kukulkán
The Temple of Kukulkán, often referred to as El Castillo, is one of the most recognizable structures in Chichén Itzá. This pyramid stands approximately 24 meters tall and is noted for its impressive architectural design, which integrates profound astronomical significance. The building is a four-sided pyramid, with each side containing 91 steps, which, when combined with the temple platform at the top, totals 365 steps—reflecting the number of days in a year. One of the most fascinating features of the Temple of Kukulkán is its alignment with celestial events. During the spring and autumn equinoxes, the setting sun casts shadows on the steps of the pyramid, creating the visual illusion of a serpent slithering down. This effect signifies the importance of Kukulkán, the feathered serpent deity, in Maya mythology.The Great Ball Court
The Great Ball Court at Chichén Itzá is the largest of its kind in Mesoamerica, measuring an impressive 168 meters in length. The court is framed by two large walls adorned with intricate carvings and reliefs that depict scenes of the Mesoamerican ballgame and associated rituals. Played with a rubber ball, this game held profound significance beyond mere sport, serving as a form of socio-political expression and religious ceremony. The design of the ball court features sloped sides to enhance the acoustics, allowing spectators to hear the sounds of the game clearly. The sport’s importance is further exemplified by the presence of stone rings set high on the walls, through which players aimed to pass the ball. The court not only served as an athletic venue but also played a role in promoting unity among the surrounding city-states.The Sacred Cenote
The Sacred Cenote is a natural sinkhole that served as a site for religious rituals and offerings to the gods. This cenote, with its deep turquoise waters, was believed to be a gateway to the underworld. Archaeological discoveries suggest that many valuable objects, including gold, jade, and pottery, were thrown into the water as ceremonial offerings. Its significance in Maya culture goes beyond its physical appearance. The cenote is a vital source of water, crucial for sustaining the surrounding population in a region where surface water is scarce. Today, it remains a site of reverence, attracting visitors who seek to understand its historical mystique.The Temple of the Warriors
The Temple of the Warriors is a notable example of the architectural fusion between Maya and Toltec styles. This temple complex features a series of columns, many of which are intricately carved with warrior motifs, showcasing the cultural interplay between these two civilizations. The temple is characterized by a large platform and a staircase leading to the sacrificial altar associated with various deities. The warrior imagery depicted throughout the temple hints at the militaristic values upheld by the society at the time. The intricate reliefs serve as both decorative elements and historical records of the region’s conquests and battles. The alignment of the Temple of the Warriors with celestial bodies further emphasizes its importance in religious and ceremonial practices.
The warrior imagery depicted throughout the temple hints at the militaristic values upheld by the society at the time. The intricate reliefs serve as both decorative elements and historical records of the region’s conquests and battles. The alignment of the Temple of the Warriors with celestial bodies further emphasizes its importance in religious and ceremonial practices.
Chichén Itzá’s Place in the Yucatán Peninsula
Chichén Itzá holds a pivotal position within the Yucatán Peninsula, not just as a historical site, but also in terms of its geographic and cultural influence. This section explores the site’s geographical significance and its recognition as a World Heritage site.Geographic Importance
Located in the municipality of Tinúm, in the state of Yucatán, Chichén Itzá enjoys a strategically advantageous position. It lies approximately halfway between the two major cities of Mérida and Cancún, making it a central point for both tourism and commerce.- The location is close to major transportation routes, facilitating access for visitors.
- Proximity to cenotes, natural sinkholes that provided fresh water, contributed to the city’s longevity and development.
- Surrounded by lush tropical forests, the site is not only rich in history but also in biodiversity.
Chichén Itzá as a World Heritage Site
In 1988, UNESCO designated Chichén Itzá as a World Heritage Site, recognizing its cultural and historical significance. This acknowledgment highlights the site’s outstanding universal value and the necessity for its preservation.- The site exemplifies the architectural marvels of the Maya civilization and reflects their advanced understanding of astronomy and engineering.
- It serves as a vital marker of the cultural exchanges between the Maya and Toltec civilizations, illustrating their influences on architecture and art.
- The designation as a World Heritage Site underscores the importance of conserving such landmarks for future generations.
Chichén Itzá Compared to Other Mayan Ruins
When exploring the wonders of the Mayan world, Chichén Itzá holds a prominent place. However, there are several other remarkable sites in the Yucatán Peninsula worth considering for their unique characteristics and historical significance.Ek Balam: Unique Features and Attractions
Ek Balam, meaning «Black Jaguar» in the Mayan language, is known for its stunning architectural features and well-preserved structures, set in a lush jungle environment.- The Acropolis: This enormous structure features intricate stone carvings and is the most significant pyramid in Ek Balam. Its unique façade displays a wealth of jaguar motifs, emphasizing the site’s cultural importance.
- Stelae and Altars: Numerous well-preserved stelae can be found here, depicting elaborate scenes of the rulers and deities, providing insight into the site’s history.
- Ball Game Court: Like many Mayan sites, Ek Balam features a ball court that serves as evidence of its recreational and cultural practices.
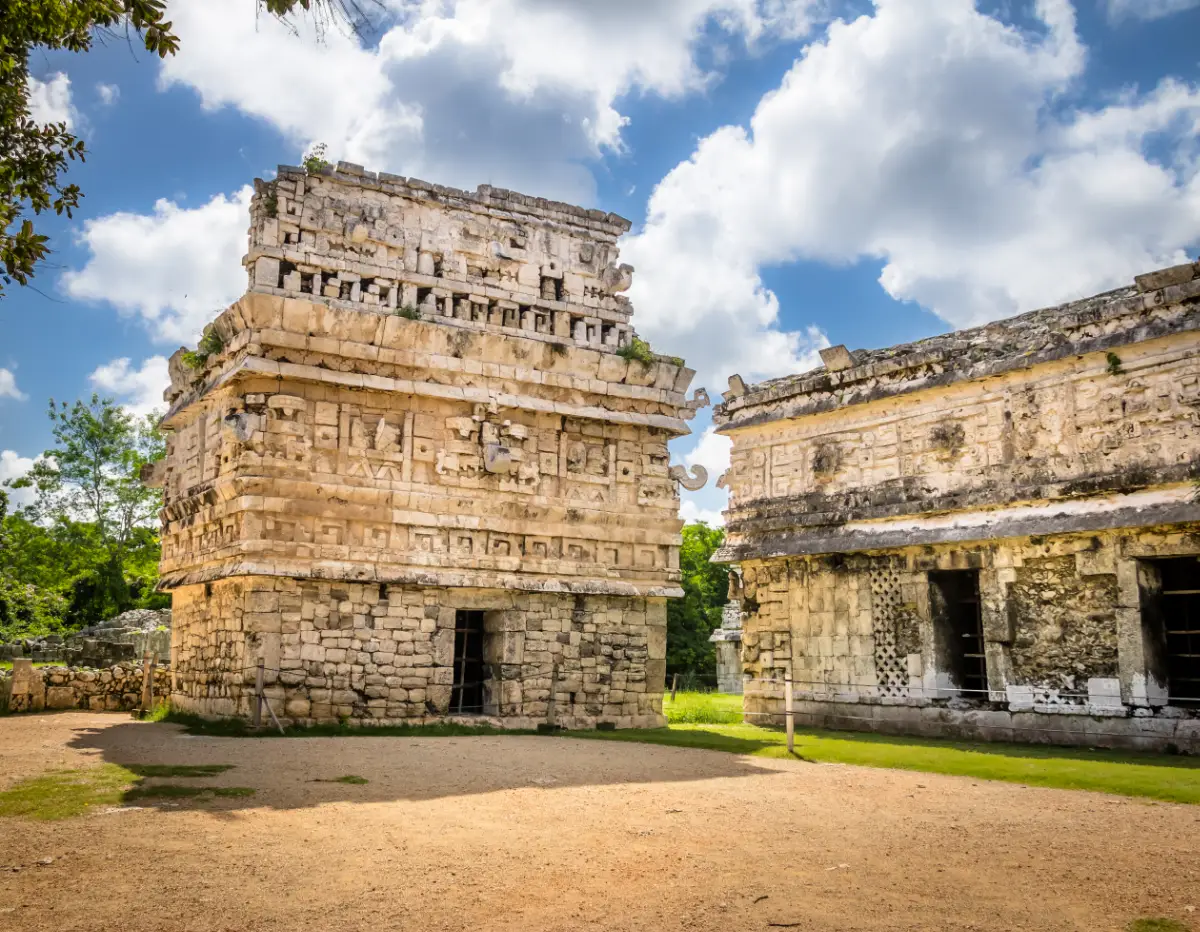

Uxmal: Architectural Significance
Uxmal is renowned for its beautiful and sophisticated architectural style, reflecting the Puuc tradition. This site offers some of the most ornate constructions in the Mayan world.- The Pyramid of the Magician: This iconic structure stands out due to its unique elliptical shape. It is surrounded by legends, including tales of magical lore tied to its construction.
- The Governor’s Palace: This extensive building features stunning stone mosaics and intricate carvings, representing the skill and artistry of Mayan architects.
- The Great Pyramid: A notable feature of Uxmal, it boasts a series of steep steps and a carefully designed layout that showcases the site’s astronomical alignments.
Tulum: Coastal Beauty and Historical Context
Tulum stands out not only for its historical significance but also for its breathtaking coastal views. Situated on cliffs overlooking the Caribbean Sea, it offers a unique blend of natural beauty and archaeological intrigue.- El Castillo: The most famous structure at Tulum, this pyramid served as a lighthouse for ancient sailors. Its strategic location made it an important trading port for the Mayans.
- The Wall: Tulum is one of the few walled cities built by the Mayans. The well-preserved walls showcase the defensive architecture that protected the inhabitants from invaders.
- The Temple of the Frescoes: This building displays remarkable murals that depict various deities, serving as a testament to the artistry and spiritual beliefs of the Mayan culture.
Visiting Chichén Itzá and Nearby Sites
Exploring Chichén Itzá provides an enriching experience for travelers interested in ancient civilizations. Visitors should take into consideration various aspects, including planning their trip, accessibility, and the surrounding attractions that enhance the experience of the Yucatán Peninsula.Planning Your Visit to Chichén Itzá
Before heading to this iconic site, careful planning can greatly enhance the overall experience. It is recommended to consider the following:- Optimal time of year: The best time to visit is during the dry season, which typically runs from November to April. This period offers pleasant temperatures and fewer chances of rain.
- Time of day: Arriving early in the morning allows visitors to avoid the peak tourist crowds, providing a more intimate experience with the ruins.
- Guided tours: Opting for a guided tour can provide in-depth insights into the history, architecture, and cultural significance. Many tours include transportation from nearby cities.
- Duration of visit: Planning to spend at least half a day allows ample time to explore the main attractions within the site.
Tourist Accessibility and Amenities
Chichén Itzá is well-equipped to accommodate visitors, ensuring a comfortable experience. Accessibility options include:- Transportation: The site is reachable via major roads from nearby cities such as Mérida and Cancún. Public buses and private transport options are readily available.
- Facilities: Amenities such as restrooms, restaurants, and souvenir shops are located near the entrance, making it convenient for tourists.
- Parking: A large parking area is available for those traveling by car, providing easy access to the site.
- Accessibility for disabled visitors: The site is largely accessible, with pathways designed for those with mobility challenges.
Experiencing the Yucatán Peninsula
Visiting Chichén Itzá offers not only a glimpse into the ancient Maya civilization but also serves as a gateway to the broader Yucatán Peninsula experience. Several nearby attractions enhance the travel experience:- Ek Balam: Famous for its well-preserved ruins and stunning views from the main pyramid, Ek Balam offers a unique perspective on Maya civilization.
- Uxmal: Renowned for its intricate architectural designs and significant historical context, Uxmal provides a different example of Maya innovation.
- Tulum: This coastal site features breathtaking views of the Caribbean Sea, highlighting the strategic significance of trading routes in ancient times.
- Cenotes: The Yucatán Peninsula is dotted with cenotes, or natural sinkholes, which offer opportunities for swimming and exploration of the geological wonders of the region.
Challenges and Preservation of Chichén Itzá
Chichén Itzá faces significant challenges that threaten its preservation and integrity as one of the most important archaeological sites in Mexico. Balancing the needs of tourism with the necessity of conservation is crucial for maintaining this historical landmark.Conservation Efforts by Mexican Authorities
The Mexican government, particularly through the Instituto Nacional de Antropología e Historia (INAH), is heavily involved in the preservation of Chichén Itzá. Their efforts are aimed at ensuring that the site remains a valuable resource for future generations. Key measures include:- Regular maintenance and restoration of monuments to prevent deterioration.
- Strict regulations on tourism to limit wear and tear on the structures.
- Collaboration with international organizations for financial and technical support for conservation projects.
- Periodic assessments of the structural integrity of major buildings and monuments.
Managing Tourism and Sustainability
Tourism is vital for the local economy, yet the influx of visitors poses a threat to Chichén Itzá’s preservation. Managing this flow of tourists is essential for sustainability. Strategies include:- Implementing timed entry tickets to control the number of daily visitors.
- Developing designated pathways to reduce foot traffic on sensitive areas.
- Providing guided tours that educate visitors about the site’s significance and the need for respectful behavior.
- Promoting off-peak visiting times to lessen congestion and environmental impact.
Future Challenges
Looking ahead, various challenges remain. Climate change poses a significant risk, as rising temperatures and increased rainfall can lead to erosion and other damages. Ongoing monitoring and adaptive strategies will be necessary to address these evolving threats. Additionally, the engagement of local communities and stakeholders in preservation efforts is crucial. This involvement can help foster long-term commitment to safeguarding Chichén Itzá and ensure that its legacy endures.Chichén Itzá: Wonder of the Ancient Mayan World
Now that you know the history, it's time to live it. Go beyond the crowds and experience Chichén Itzá's true magnificence with our expert local guides.