Spider monkeys are vital primates that play an essential role in tropical ecosystems. They contribute to biodiversity by aiding in seed dispersal, which helps maintain forest health. Despite their importance, spider monkeys face numerous threats, including habitat loss and the illegal pet trade. Effective conservation efforts are crucial to ensure their survival and support local communities involved in their protection.
Understanding Spider Monkeys
To appreciate the necessity of conserving spider monkeys, it is essential to understand their unique characteristics and social behavior.
Characteristics of the Spider Monkey
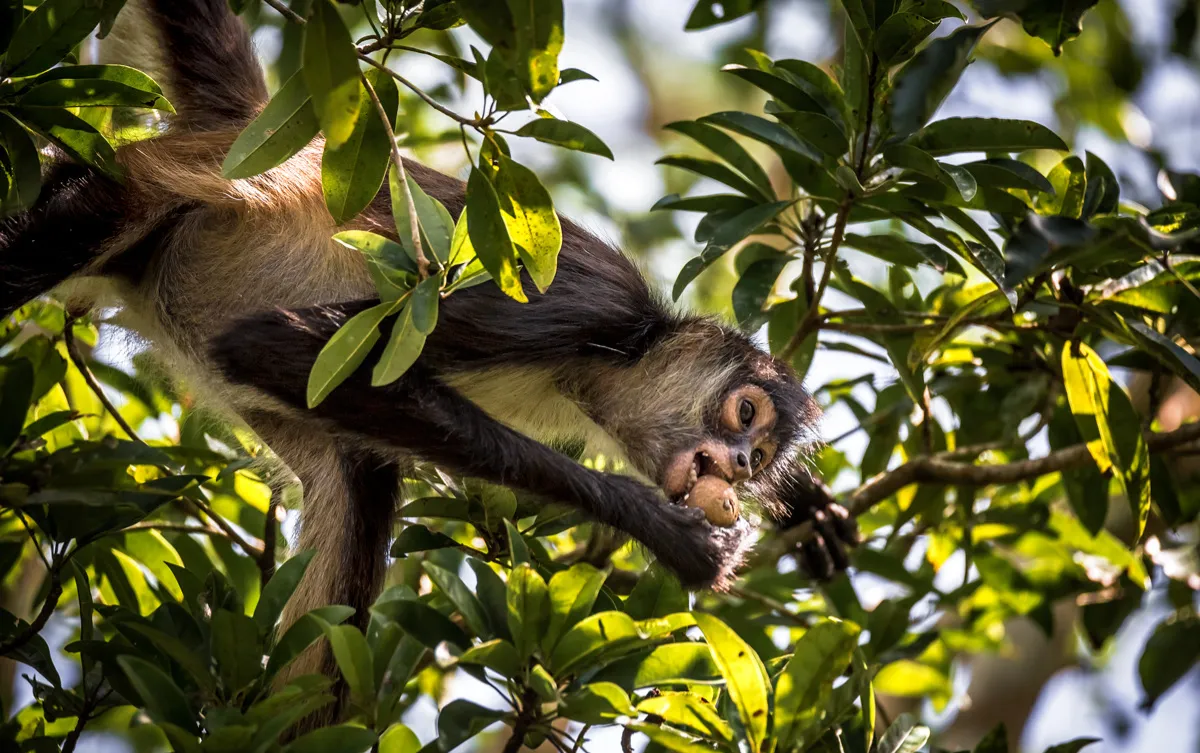
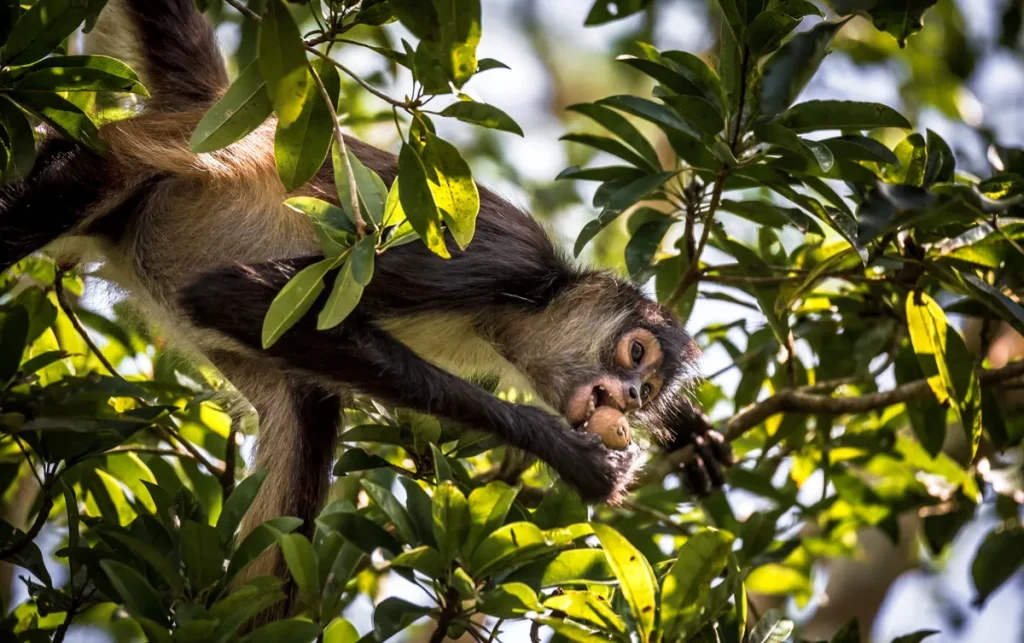
Spider monkeys are recognized for their long limbs and prehensile tails, which are adaptations that facilitate their arboreal lifestyle. Their body length ranges from 60 to 90 centimeters, not including their tails, which can be as long as their bodies. These primates are typically agile and can swing from branch to branch with ease.
Their physical appearance varies, featuring slender bodies, long limbs, and a distinctive facial structure. Their fur is usually dark with variations depending on the species, providing them with camouflage in the forest canopy.
Species and Variations
Ateles Geoffroyi
This species is commonly found in Central America, particularly in countries like Costa Rica and Guatemala. Notable for their sociable nature, they often travel in groups ranging from 20 to 35 individuals. Their vocalizations are distinct, aiding communication among group members.
Ateles Hybridus
Native to the forests of Colombia and Venezuela, Ateles hybridus is critically endangered. Their habitat has been significantly altered due to deforestation. They share similar behavioral traits with other spider monkey species, often forming tight-knit communities that rely on each other for protection and social bonding.
Behavior and Social Structure
Spider monkeys are highly social creatures that exhibit complex interactions within their groups. They engage in grooming behaviors, which reinforce social bonds. These monkeys are also known for their loud calls, which serve multiple functions, such as alerting group members to potential threats and coordinating movement through the forest.
Life in groups not only provides safety in numbers but also facilitates the teaching of foraging skills and navigation of their environment to younger members. The matriarchs often lead these groups, showcasing a level of social hierarchy that is prevalent in their communities.
The Role of Spider Monkeys in Ecosystems
Spider monkeys play a crucial role in sustaining the health and diversity of tropical ecosystems. Their unique behaviors and dietary habits contribute significantly to the functionality of the forests they inhabit.
Contribution to Tropical Rainforests
As highly social primates, spider monkeys rely primarily on a frugivorous diet, meaning they consume a lot of fruit. This feeding behavior has several impacts on their native environments. By foraging and eating various fruits, they help in the natural process of seed dispersal. When they consume fruit, they often travel great distances, excreting seeds in different locations. This not only aids in the growth of new plants but also encourages genetic diversity within plant populations.
The presence of spider monkeys in rainforests is an indicator of ecological health. Their activity supports a balanced ecosystem by influencing forest structure and regeneration. The continuous movement of these monkeys through the canopy also helps maintain the integrity of the forest surfaces, impacting plant community composition over time.
Impact on Biodiversity and Seed Dispersal
Seed dispersal is a vital ecosystem service that spider monkeys facilitate. They are known to produce large quantities of seeds through their diet, which contributes to forest regeneration. This process is essential for maintaining biodiversity. By enabling various plant species to thrive, spider monkeys help create an environment that supports other wildlife, enhancing overall biodiversity.
- Spider monkeys help sustain the following aspects of biodiversity:
- Plant Diversity: Supporting the growth of various plant species ensures that ecosystems remain resilient to changes and disturbances.
- Animal Habitats: Diverse plant communities provide habitat and food resources for numerous other animal species.
- Ecological Balance: The interactions between spider monkeys and their environment help maintain ecological balance, benefiting the entire forest ecosystem.
Ultimately, the role of spider monkeys is integral to the health of tropical rainforests. Their unique contributions to seed dispersal and the maintenance of biodiversity showcase their importance to the ecosystems in which they live.
Threats to Spider Monkeys
Spider monkeys face several significant threats that jeopardize their survival in the wild. These dangers arise from human activities and environmental changes, amplifying the need for focused conservation efforts.
Deforestation and Habitat Loss
One of the most pressing challenges for spider monkeys is deforestation, primarily driven by agricultural expansion and urban development. As forests are cleared for crops or livestock, the natural habitats of these primates are increasingly fragmented.
This loss of habitat not only reduces their living space but also limits their access to food sources, which consist mainly of fruits found in mature forests. Consequently, the fragmentation makes it difficult for monkey populations to interact, breed, and maintain genetic diversity, further threatening their survival.
The Pet Trade and Hunting
The illegal wildlife trade poses a major risk to spider monkey populations. In many regions, these monkeys are captured for the exotic pet market. Young monkeys are often taken from their mothers, resulting in high mortality rates for both the infants and their mothers during the capture process.
- Capturing spider monkeys disrupts social structures, as they typically live in family groups and depend on social bonds.
- Hunting for local consumption also contributes to population declines, especially in areas where they are hunted unsustainably.
These factors combine to weaken their populations, creating a cycle that makes recovery increasingly challenging.
Climate Change
The impacts of climate change further exacerbate the threats to spider monkeys. Alterations in weather patterns lead to unpredictable food availability and habitat conditions. Droughts and increased temperatures can affect the growth of fruit trees crucial to their diet.
Furthermore, climate change can disrupt migration patterns and the ecological balance of the tropical forests where spider monkeys thrive. As their habitats become less fertile and more inhospitable, these monkeys will likely face increased competition for reduced resources.
Efforts to conserve spider monkeys are multifaceted and involve collaboration among various organizations, local communities, and initiatives focused on sustainable practices. These concerted actions aim to address the threats facing these primates and ensure their survival.
Conservation Efforts
Key Initiatives and Organizations
Numerous initiatives are dedicated to the conservation of spider monkeys, focusing on habitat restoration, community engagement, and research. These programs often include non-profit organizations that specialize in wildlife conservation, local governments, and international partnerships. Key players in this field include:
- Conservation International: Promotes biodiversity and sustainable practices through community programs.
- Wildlife Conservation Society: Focuses on research and habitat protection efforts.
- Local NGOs: Operate specific conservation initiatives tailored to the needs of local communities and wildlife.
Local Community Involvement
Community engagement is crucial in conservation strategies. Local populations play a vital role in protecting spider monkeys and their habitats. Educational initiatives aim to inform communities about the ecological importance of these primates, fostering a culture of stewardship.
Sustainable Practices in Yucatán
In the Yucatán region, sustainable agricultural practices are being promoted to reduce deforestation and habitat encroachment. These methods not only preserve the forest but also enhance the livelihoods of farmers. Soil conservation techniques, agroforestry, and organic farming are being implemented to ensure a balance between development and biodiversity. Local farmers are trained to:
- Implement organic farming techniques to minimize chemical use.
- Create wildlife corridors that connect fragmented habitats.
- Engage in agroforestry to diversify crops while preserving woodlands.
Success Stories and Challenges
Several successful conservation projects have emerged, demonstrating effective strategies for protecting spider monkeys. These initiatives have led to the establishment of protected areas, reforestation projects, and the rehabilitation of injured animals.
Despite these successes, challenges remain. Deforestation continues due to agricultural expansion and illegal logging. Climate change further complicates efforts, stressing the need for ongoing research and adaptive management strategies to improve conservation outcomes.
Eco Mayan Adventures and Spider Monkey Conservation
Eco Mayan Adventures plays a significant role in the conservation of spider monkeys, particularly through its eco-tourism initiatives that promote awareness and educate visitors about these vital primates.
Eco-Tourism and Conservation Awareness
This tour operator enriches guests’ understanding of local ecosystems and the importance of spider monkeys in maintaining biodiversity. By incorporating educational components into their tours, Eco Mayan Adventures highlights the interconnectedness of species and ecosystems.
Activities that may be included in eco-tours often focus on:
- Guided nature walks that reveal monkey habitats.
- Workshops on rainforest ecology and conservation.
- Discussions on the impact of deforestation and climate change.
How Tourists Can Help
Visitors not only gain knowledge but also contribute to conservation efforts through their participation. Spending time with local communities fosters positive interactions and strengthens the commitment to preserving vital habitats.
Community-Based Tourism Initiatives
Community-based tourism initiatives emphasize sustainable practices that benefit both the environment and local residents. Eco Mayan Adventures partners with indigenous communities, empowering them through economic opportunities tied to wildlife conservation.
Key benefits of these initiatives include:
- Income generation for local families through eco-friendly crafts and products.
- Education programs that teach locals about sustainable agriculture and environmental stewardship.
- Support for preservation efforts that ensure the spider monkeys’ habitat remains intact.
These efforts not only enhance the local economy but also elevate awareness on the importance of spider monkeys within their ecological context. By connecting visitors with local conservation initiatives, Eco Mayan Adventures fosters a sense of shared responsibility in preserving these remarkable animals for future generations.
Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research plays a vital role in shaping effective strategies for conserving spider monkeys and their habitats. Understanding their behavior, ecology, and the pressures they face is essential for developing innovative conservation methods.
Importance of Scientific Research
Scientific investigation provides the foundation for informed conservation practices. By studying spider monkey populations, their behaviors, and interactions with the ecosystem, researchers can identify key areas needing protection and restoration. Important aspects of research include:
- Understanding population dynamics and demographics to assess population health.
- Exploring habitat requirements and preferences to guide preservation efforts.
- Investigating the impact of human activities, such as deforestation and agriculture, on spider monkey habitats.
- Examining the effectiveness of current conservation strategies and suggesting improvements.
This research not only focuses on spider monkeys but also considers the overall health of their ecosystems, emphasizing the role these primates play in biodiversity and ecological balance.
Future Goals and Innovations in Conservation
Conservation strategies are evolving through technological advancements and new methodologies. Future goals for spider monkey conservation may include:
- Implementing advanced monitoring technologies, such as drone surveillance and camera traps, to track populations and their movements.
- Developing community-led conservation initiatives that integrate local knowledge with scientific research.
- Advancing habitat restoration techniques that promote ecological resilience against climate change.
- Enhancing educational programs aimed at raising awareness about the importance of spider monkeys and their habitats.
Innovative approaches, such as genetic studies and ecological modeling, will also play a significant role in guiding conservation efforts. By leveraging these advancements, stakeholders can create more effective, adaptive management plans that respond to the changing environment and address the multifaceted challenges facing spider monkeys today.
Frequently Asked Questions About Spider Monkeys
This section addresses common inquiries regarding spider monkeys, focusing on their unique traits and conservation methods.
What Makes Spider Monkeys Unique?
Spider monkeys possess distinct characteristics that set them apart from other primate species. Their long limbs and prehensile tails allow for agile movement through the canopy, making them adept at navigating their arboreal habitats. These adaptations contribute significantly to their survival in dense rainforest environments.
Socially, spider monkeys are known for their intricate group dynamics. Living in troops, they exhibit strong social bonds and communicate through vocalizations, gestures, and body language. This social structure promotes cooperation in foraging and defending their territory. Additionally, their diet primarily consists of fruits, which further emphasizes their role as important seed dispersers within the ecosystem.
How Can We Protect Spider Monkeys?
Conservation efforts aimed at protecting spider monkeys involve multiple strategies. Community engagement plays a crucial role in these initiatives, ensuring that local populations are invested in the survival of the species.
- **Habitat Preservation:** Protecting and restoring natural habitats is vital. This can involve reforestation projects and establishing protected areas to prevent deforestation.
- **Sustainable Practices:** Implementing sustainable agricultural practices helps minimize habitat destruction while providing economic benefits to local communities.
- **Education and Awareness:** Raising awareness about the ecological importance of spider monkeys fosters public support for conservation efforts. Education programs can inform communities about the impacts of habitat loss and ways to mitigate them.
- **Research and Monitoring:** Ongoing scientific research helps track spider monkey populations and understand their behaviors. This knowledge aids in formulating effective conservation strategies.
These combined approaches can significantly enhance conservation efforts, ensuring that spider monkeys continue to thrive in their natural habitats for generations to come.