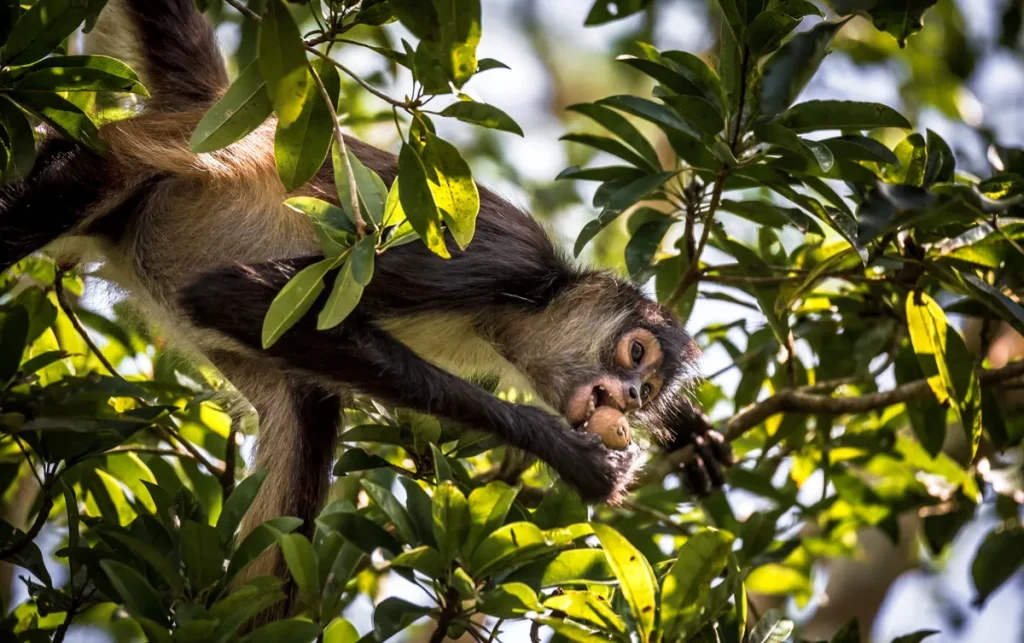
Spider monkeys in Yucatán are fascinating primates known for their agility and social behavior. They inhabit tropical and subtropical forests, playing a crucial role in the ecosystem as seed dispersers and pollinators. These monkeys face numerous threats, including habitat destruction and illegal wildlife trade. Conservation efforts are essential to protect their populations and ensure their survival in the wild.
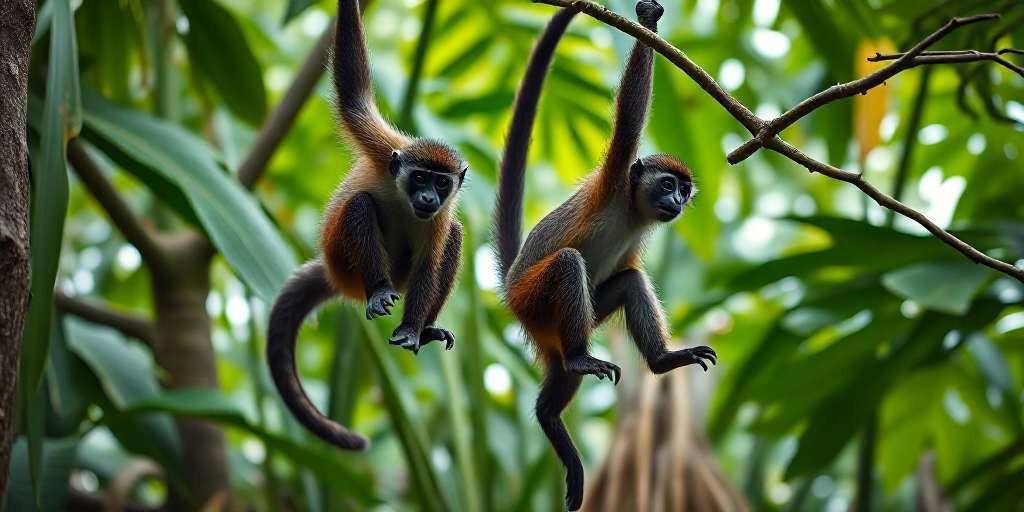




Biological Features of Spider Monkeys
Understanding the biological features of spider monkeys reveals their unique adaptations and characteristics that allow them to thrive in their environment. These remarkable primates exhibit several distinguishing traits.Physical Characteristics
Spider monkeys are notable for their elongated bodies, long limbs, and prehensile tails. Their thin, agile figures aid in maneuvering through the treetops of their forest habitats. They typically exhibit varying coat colors, ranging from black to brown or golden hues. This diversity not only adds to their visual appeal but also helps them blend into the foliage.Types and Species in Yucatan
In Yucatán, the most commonly encountered species is the Geoffroy’s spider monkey (*Ateles geoffroyi*). This species is part of a larger family that includes several other spider monkey species found throughout Central and South America. Their social structures and behavior can vary significantly among different species.Adaptations for Arboreal Life
Spider monkeys have developed several adaptations that enable their arboreal lifestyle, facilitating foraging and movement among the trees.Use of Prehensile Tail
Their prehensile tails serve as a fifth limb, providing an essential tool for grasping branches as they swing from tree to tree. This remarkable adaptation enhances their ability to navigate complex forest environments and to reach food sources that are often high in the canopy.Diet and Nutritional Needs
Primarily frugivorous, spider monkeys rely heavily on a diverse diet of fruits, which supply essential nutrients. However, they are also known to consume leaves, flowers, and occasionally insects. This varied diet enhances their role as seed dispersers within their ecosystems, which contributes to forest regeneration.Habitat and Distribution in Yucatan
The habitat and distribution of spider monkeys in Yucatan are crucial to their survival. These primates thrive in specific environmental conditions that support their dietary needs and social structures.Preferred Environments
Spider monkeys primarily inhabit tropical and subtropical forests. They are especially fond of dense, mature rainforests where tall trees provide ample canopy cover. These environments are essential for their foraging habits, as they rely on a wide array of fruits, leaves, and flowers for sustenance.Key Locations and Reserves
Yucatan is home to several important natural reserves that protect the habitat of spider monkeys. Some prominent areas include:- Ría Lagartos Biosphere Reserve
- Sian Ka’an Biosphere Reserve
Ría Lagartos Biosphere Reserve
This reserve is recognized for its rich biodiversity and serves as a critical refuge for various wildlife species, including spider monkeys. The diverse flora supports the primates’ dietary needs, allowing them to thrive in a relatively undisturbed ecosystem.Sian Ka’an Biosphere Reserve
Another vital location, Sian Ka’an boasts extensive wetlands and forests that provide spider monkeys with a safe habitat. This area is significant not only for the species itself but also for the interconnected ecosystem supporting numerous plant and animal species.Interaction with Other Wildlife
Spider monkeys are integral to their ecosystems and interact with various other wildlife species. Their role as seed dispersers enhances the biodiversity of their habitat. By feeding on fruits and subsequently excreting seeds, they contribute to the regeneration of numerous plant species. Furthermore, these primates often share their habitat with other animals, including various bird species and mammals, creating a dynamic web of interactions within the forest environment.Social Behavior and Group Dynamics
Understanding the social behavior and group dynamics of spider monkeys provides insight into their ecological roles and interactions within their environments. These primates exhibit complex social structures and unique communication methods that facilitate their interactions.Family Structures and Social Hierarchy
Spider monkeys maintain a social structure characterized by family groups that typically consist of a dominant male, several females, and their offspring. Such family groups can range from 20 to 30 individuals, depending on environmental conditions and resource availability. The social hierarchy within these groups plays a critical role in their dynamics. Dominant males often have preferential access to mates and food, influencing mating success and overall group stability. Female alliances may form, and they often support each other during social interactions, which can lead to cooperative behaviors, such as grooming and foraging.Communication Methods
Effective communication within spider monkey groups is essential for maintaining social bonds and coordinating activities. They employ various methods to convey information, which include vocalizations, gestures, and postures.Vocalizations
The vocal repertoire of spider monkeys includes a variety of calls used for different purposes, such as alarm calls to alert the group to potential threats or long-distance calls to maintain contact with members of the troop. These vocalizations are instrumental in coordinating movements and activities within the group, especially in dense forest environments where visibility is limited.Gestures and Postures
Non-verbal communication also plays a significant role in their interactions. Spider monkeys use a range of gestures, such as reaching out with their arms or subtle body movements, to express emotions and intentions. Postures can signal aggression, submission, or playfulness, helping to maintain social order and reduce conflicts within the group. These intricate communication methods highlight the intelligence and adaptability of spider monkeys, showcasing the importance of social cohesion in their survival and well-being.
Threats to Spider Monkeys
Spider monkeys face numerous threats that jeopardize their survival in the wild. These challenges range from habitat destruction due to human activities to illegal trade and environmental issues. Understanding these threats is crucial for implementing effective conservation strategies.Habitat Destruction
The loss of natural habitats is one of the most significant threats to spider monkey populations. This destruction is primarily driven by two main factors:Deforestation
Deforestation has led to the rapid decline of forest areas essential for spider monkeys. The clearing of land for agriculture and logging disrupts their natural living conditions. As trees vanish, these primates lose both their shelter and food sources, affecting their survival rates.Urban Expansion
Urban development has also contributed to habitat loss. As cities grow, forests are replaced by roads, buildings, and infrastructure. This encroachment not only limits the available territory for spider monkeys but also fragments their populations, making it harder for them to find mates and food.Illegal Wildlife Trade
The illegal wildlife trade poses a severe risk to spider monkeys. Due to their appealing appearance and social nature, they are sought after as exotic pets. This demand leads to poaching and trafficking, disrupting their natural populations. Captured monkeys often suffer from poor living conditions and high mortality rates during transportation.Environmental Challenges
Environmental factors also threaten the stability of spider monkey populations. These issues are increasingly becoming a concern:Climate Change Effects
Climate change has introduced significant challenges, affecting food availability and habitat conditions. Changes in temperature and rainfall patterns can lead to food shortages for spider monkeys. Moreover, extreme weather events can destroy their forest habitats, complicating their survival even further.Pollution
Pollution presents another danger that impacts spider monkeys directly and indirectly. Contaminants can affect their food sources. Pollution in rivers and water bodies can lead to the bioaccumulation of toxic substances in the plants and fruits they consume. This not only impacts their health but also the entire ecosystem they rely on.Conservation Efforts in Yucatan
Efforts to conserve the spider monkeys in Yucatán are vital to maintaining the region’s biodiversity. Various programs and initiatives are underway to protect their habitat and ensure their survival.Reforestation Programs
Reforestation is a critical step in restoring the natural habitat for spider monkeys. These initiatives focus on planting native species of trees that provide food and shelter for wildlife. Local communities are often involved in these efforts, helping to restore the ecosystem while gaining economic benefits.- Community nurseries have been established to grow indigenous tree species.
- Educational workshops inform residents about the ecological importance of trees.
Anti-Poaching Legislation
Legal frameworks have been developed to combat poaching and illegal wildlife trade. Anti-poaching legislation aims to deter threats to spider monkeys by imposing strict penalties on offenders. Enforcement of these laws is critical for their effectiveness.- Increased patrolling in critical habitats helps catch poachers in the act.
- Collaboration with local law enforcement enhances support for anti-poaching efforts.
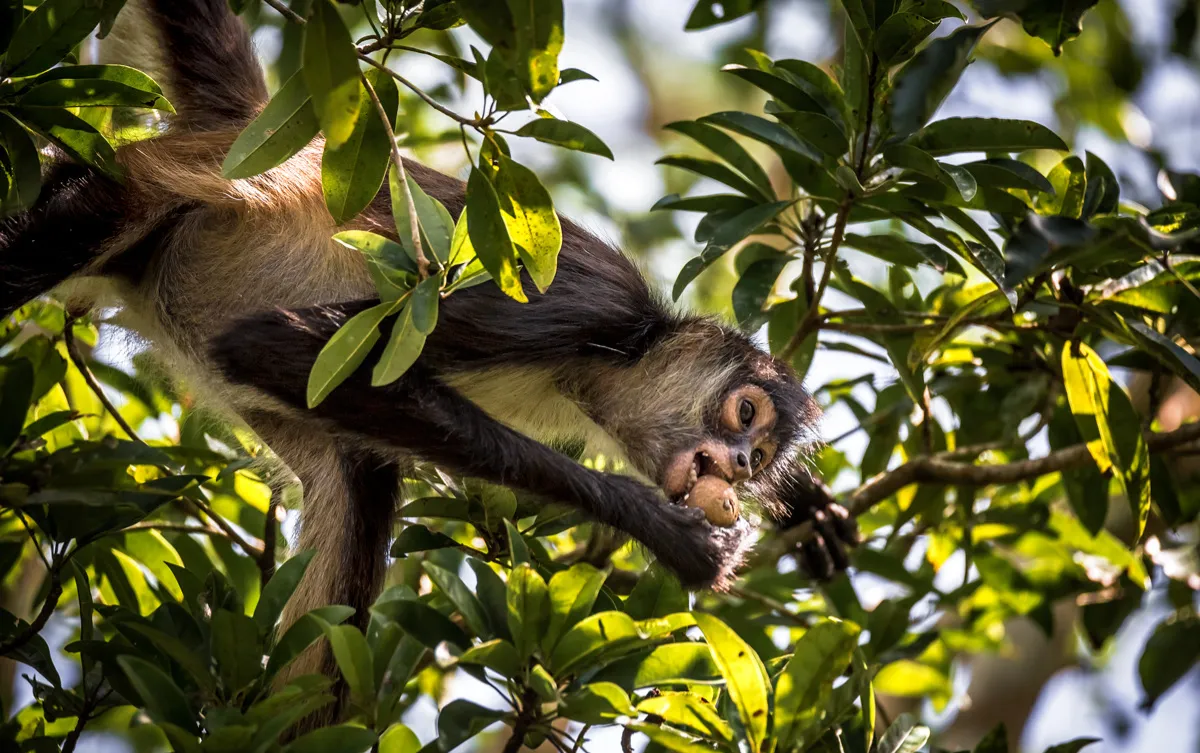

Role of Local Organizations
Local organizations play a pivotal role in conservation efforts, working closely with communities and governments to protect spider monkeys. Their initiatives vary from direct intervention to educational programs aimed at enhancing local engagement in conservation.Foundation for Primate Conservation
This prominent organization is dedicated to the protection of primates in Yucatán. Their work includes field research, habitat protection, and community outreach initiatives.- They organize volunteer programs for monitoring monkey populations.
- Training sessions enable local residents to become wildlife advocates.
Community Involvement
Empowering local communities is crucial for the success of conservation efforts. By involving residents as stakeholders, conservation initiatives gain greater support and efficacy.- Community-based ecotourism programs provide alternative income sources that reduce reliance on illegal activities.
- Local traditions and knowledge are integrated into conservation strategies to enhance community engagement.
Cultural Significance in Yucatan
The cultural importance of spider monkeys in Yucatán resonates deeply within local communities. These remarkable animals are woven into the fabric of folklore, art, and daily life, illustrating the rich biodiversity of the region.Myths and Legends
Spider monkeys have inspired various myths and legends that reflect the beliefs and traditions of the local communities. In many indigenous narratives, these primates are depicted as tricksters or guardians of the forest. Their agility and playful nature lend themselves to stories emphasizing the relationship between humans and nature.- Some tales attribute special powers to spider monkeys, suggesting they are messengers between the natural world and human beings.
- Legends often highlight the importance of protecting these creatures, serving as a reminder of the responsibility humans have toward the environment.
Representation in Art and Crafts
In Yucatán, spider monkeys frequently appear in various forms of artistic expression. Local artisans draw inspiration from these primates, incorporating them into intricate designs and crafts.- Traditional textiles often feature spider monkey motifs that celebrate the region’s wildlife.
- Stone carvings and pottery may depict these animals, connecting cultural heritage with the natural surroundings.
- Spiritual symbolism in art communicates themes of harmony and balance, reflecting the respect for spider monkeys as essential wildlife.
The Impact of Ecotourism
Ecotourism has emerged as a significant force in the conservation efforts for spider monkeys in Yucatán. This approach offers unique advantages that not only promote environmental preservation but also foster meaningful interaction between local communities and biodiversity.Benefits for Conservation
Through ecotourism, local ecosystems benefit in various ways. The influx of visitors generates funds that can support conservation programs and enhance habitat protection. These proceeds can be directed toward:- Reforestation initiatives that restore natural habitats.
- Education programs that raise awareness about the importance of local wildlife.
- Support for community-driven conservation efforts that involve local stakeholders.
Guidelines for Responsible Tours
Implementing responsible tourism practices is essential for minimizing negative impacts on spider monkeys and their habitats. Guidelines are crucial to ensuring that ecotourism benefits both wildlife and local communities.Minimizing Human Impact
To reduce human disturbances, it’s vital for tours to adhere to specific guidelines. Tour operators should:- Limit the number of visitors in sensitive habitats at any given time.
- Establish designated pathways to minimize habitat trampling.
- Enforce strict policies against feeding or attempting to interact with wildlife.
Educating Tourists
Effective education programs for tourists can significantly enhance ecotourism experiences. Informative initiatives can focus on:- Teaching tourists about the ecological role of spider monkeys in their ecosystems.
- Explaining the challenges these species face and the importance of conservation efforts.
- Encouraging responsible behavior to protect both wildlife and the environment.
Research and Educational Initiatives
Efforts to understand and protect spider monkeys in Yucatán involve both scientific research and community education. These initiatives aim to promote awareness and encourage local participation in conservation.Ongoing Studies on Behavior
Current research focuses on various aspects of spider monkey behavior, including social interactions, foraging habits, and communication methods. Understanding these behaviors is crucial for effective conservation strategies.- Behavioral patterns reveal how spider monkeys interact within their social groups.
- Studies on foraging highlight their dietary needs and preferences.
- Research on vocalizations helps document their communication styles and social cues.
Educational Programs for Schools
Education plays a pivotal role in fostering a culture of conservation. Programs designed for schools aim to engage students and educators alike in understanding the importance of biodiversity and the specific needs of spider monkeys.Promoting Biodiversity Awareness
Through interactive activities and workshops, students learn about the rich ecosystems of Yucatán and the role spider monkeys play within these environments. These initiatives inspire a sense of responsibility toward environmental stewardship.- Workshops include hands-on activities focusing on ecology and conservation.
- Programs involve field trips to local reserves, allowing students to observe wildlife firsthand.
- Educational materials are provided to reinforce learning objectives in classrooms.
Encouraging Community Participation
Community involvement is essential for successful conservation efforts. Programs encourage families and local residents to participate in activities that support the preservation of spider monkeys and their habitats.- Volunteering opportunities in local conservation projects help build a strong community commitment.
- Workshops promote sustainable practices that can be adopted by households.
- Community events highlight local biodiversity and the significance of spider monkeys in Yucatán’s culture.
Future Projections for Spider Monkey Conservation
Successes and Ongoing Challenges
Over recent years, there have been notable achievements in spider monkey conservation in Yucatán. Several local organizations have effectively raised awareness and implemented successful reforestation projects. These initiatives have helped restore parts of their natural habitats, providing essential resources for food and shelter.- Increased community engagement has led to grassroots efforts that empower locals to participate in conservation activities.
- Educational programs have enhanced understanding of the species and its ecological importance.
Collaborative Efforts and Innovations
Effective conservation relies heavily on collaborative efforts among governmental, non-governmental organizations, and local communities. Partnerships have been formed to create comprehensive plans that address both the ecological needs of spider monkeys and the social needs of local populations. These collaborations foster mutual benefits, balancing wildlife preservation with community development.- Joint research initiatives are being conducted to monitor populations and assess the health of their ecosystems.
- Funding opportunities from international organizations have supported innovative conservation techniques, such as wildlife corridors that connect fragmented habitats.
Your Jungle Adventure Awaits
Now that you understand their importance and the challenges they face, you can be part of the solution. Support responsible ecotourism and see spider monkeys in the wild with us. Your visit to Punta Laguna directly helps the community that protects them. Book your conservation adventure today!